Learning Outcomes
i. Define carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
ii. Explain the importance of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids to life.
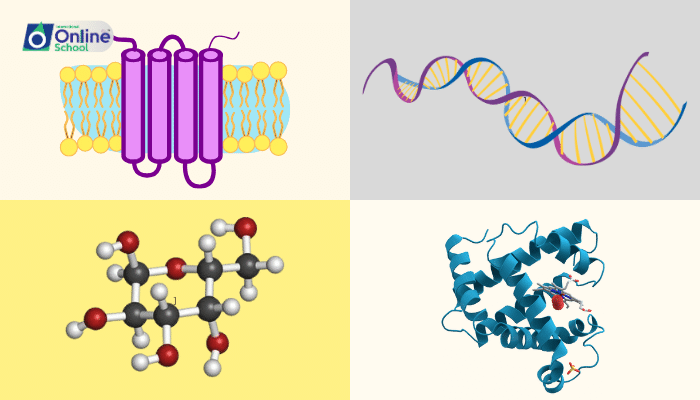
i. Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for cells. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose. Monosaccharides can be linked together to form disaccharides, such as sucrose (table sugar), and polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen.Carbohydrates are important for life because they provide energy for cells to function. They are also used to build cell walls and other structures in plants and bacteria.
ii. Proteins: Proteins are the building blocks of cells and tissues. They are made up of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. There are 20 different amino acids that can be used to build proteins. Proteins are important for life because they are involved in all aspects of cell structure and function. They are involved in metabolism, cell signaling, gene expression, and the immune system.
iii. Lipids: Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Lipids include fats, oils, and waxes. Lipids are important for life because they are used to store energy, build cell membranes, and produce hormones.
iv. Nucleic acids: Nucleic acids are the molecules that store and transmit genetic information. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. DNA is the genetic material that is passed from parents to offspring. RNA is involved in protein synthesis and other cellular processes. Nucleic acids are essential for life because they contain the instructions for building and maintaining cells.
v. Relationship between the four fundamental kinds of biological molecules
The four fundamental kinds of biological molecules are all interconnected. For example, carbohydrates are used to generate energy, which is used to synthesize proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Proteins are involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Lipids are used to build cell membranes, which are essential for the transport of carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. Nucleic acids encode the instructions for building and maintaining cells, which are made up of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Real-world applications of the four fundamental kinds of biological molecules:
The four fundamental kinds of biological molecules are used in a wide range of products and industries. For example, carbohydrates are used in food, biofuels, and pharmaceuticals. Proteins are used in food, pharmaceuticals, and industrial enzymes. Lipids are used in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Nucleic acids are used in diagnostic tests, gene therapy, and vaccines.The four fundamental kinds of biological molecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These molecules are essential for life because they are involved in all aspects of cell structure and function.